What is basis?

The Snapshot
- The term basis confuses many. It is however, merely the difference (positive or negative) between the physical and futures price.
- The basis generally refers to CBOT and local, however, could be with any other futures exchange.
- The biggest driver of basis is the local supply of grains.
- If supplies are low, then basis rises. Conversely, a large crop tends to lead to lower basis levels.
The Detail
The term basis is regularly used in the grain industry. What does it mean?
One of the most common questions which I am asked is ‘what is basis?’. It is a jargon word which confuses many. In reality, the term basis is quite simple.
The price offered by your local grain buyer is quoted as a flat price, this is the price for the physical delivery of grain, with all the components of pricing included. An example would be A$310/mt delivered Melbourne, and this price includes futures, fx and basis.
In future updates, I will discuss the other components of FX & futures in more detail, with this focus of this article on basis.
The term basis is exchangeable with difference. When someone is talking about basis, they are discussing the difference between two different prices, generally between physical and futures.
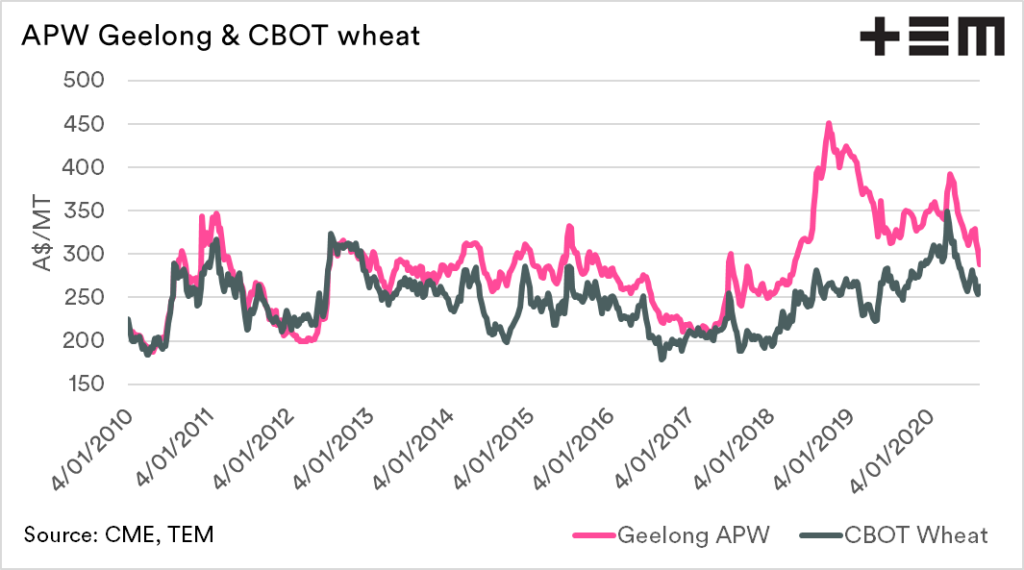
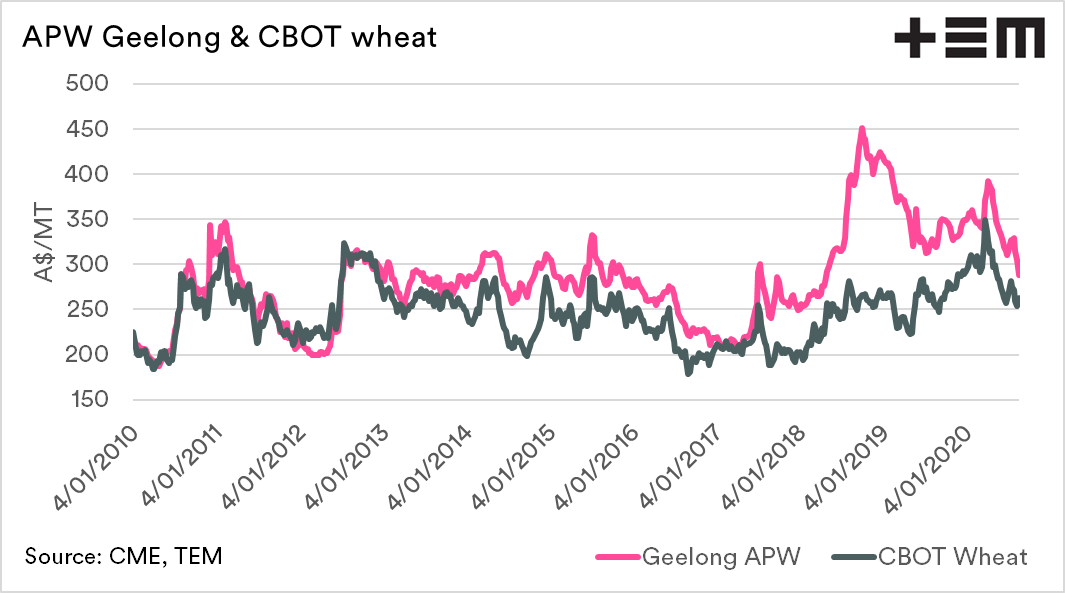
In general, in Australia, basis is a comparison of against CBOT soft red winter wheat (in A$/MT). Although whether CBOT is the relevant indicator is a discussion for another day.
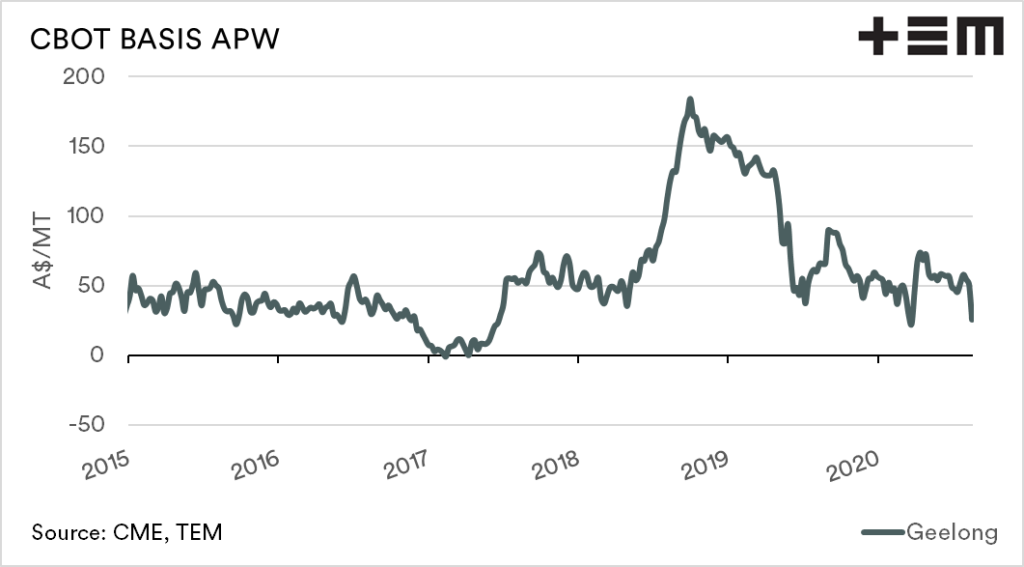
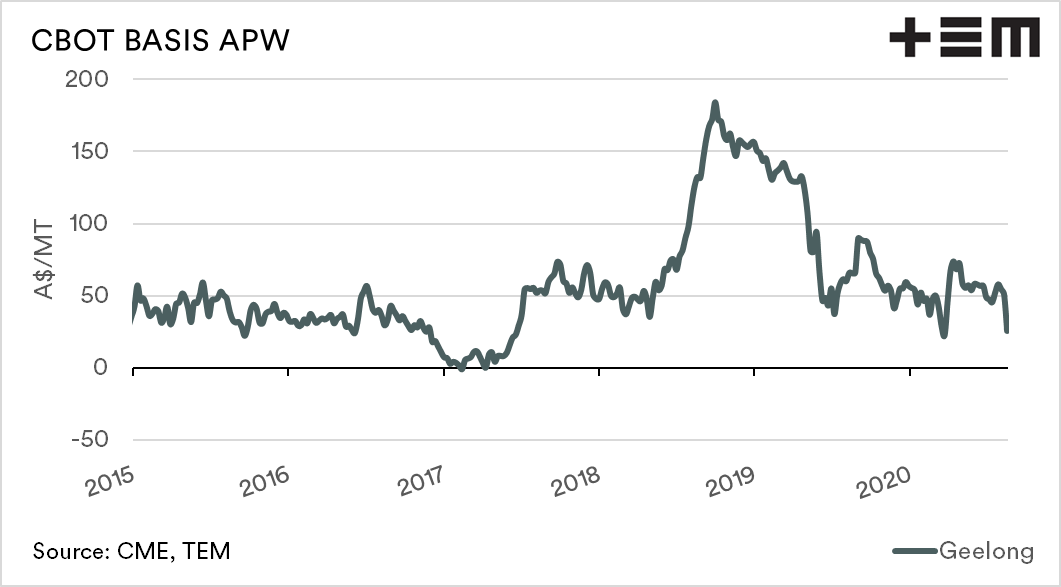
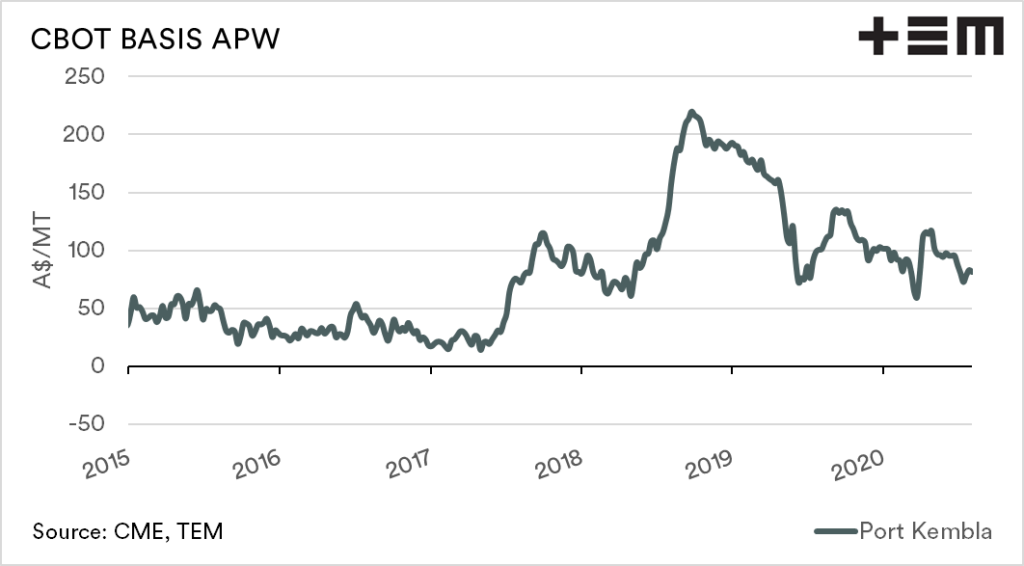
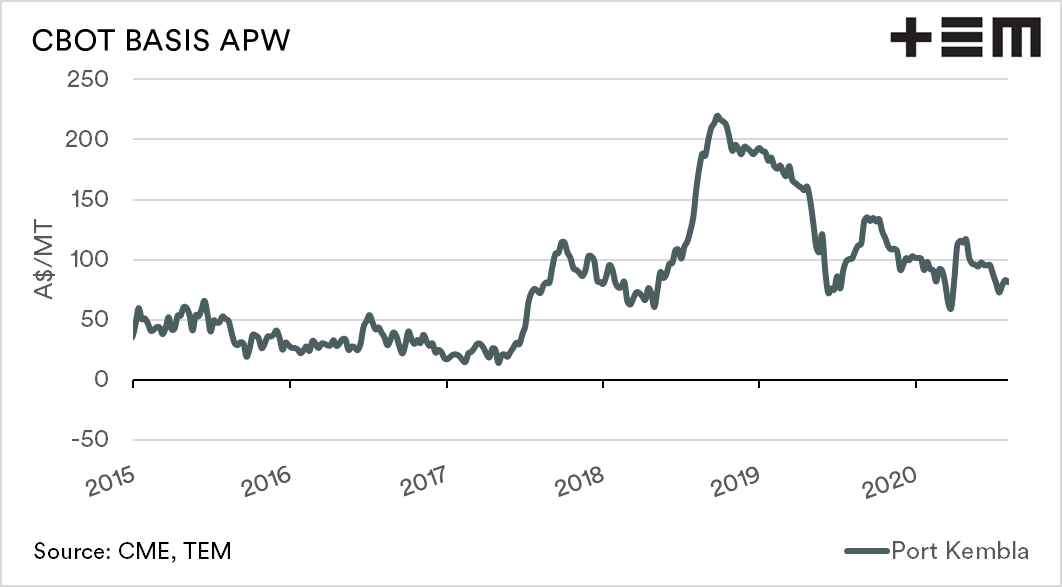
The basis level can be either positive (premium) or negative (discount) to CBOT futures. Australian basis levels tend to be positive, with very minimal time at neutral or negative levels.
What drives basis?
The largest driver of basis levels is the local supply of grain. Recent years have seen basis levels rise to record levels. The premium was due to the drought-induced deficit of grain on the east coast. When supply is low, the basis level tends to rise rapidly, providing producers with a very strong premium over international values.
The converse occurs when Australia has a good year. When the local supply of grain is at a large surplus, the basis level declines, as the domestic market does not have to pay up to cover requirements.
The production of grain in Australia is rebounding after a run of miserable years, with forecasts between 25-30mt+. The larger the production, the more pressure that will be placed on basis levels, and our premium versus the rest of the world will decline.
Over time a lower basis level tends to mean that production has strong. In contrast, high basis levels generally mean that the majority of farmers don’t have much to sell to capitalise on higher levels.
As we move forward to the horizon with hopefully good crops, and an uncertain market, it will be worthwhile examining basis levels.
Some additional charts: